Crm in services – Customer Relationship Management (CRM) in services is a transformative tool that empowers organizations to build stronger relationships with their customers. By leveraging CRM software and solutions, service businesses can streamline operations, improve customer satisfaction, and drive growth.
This comprehensive guide delves into the key aspects of CRM in services, providing insights into its implementation, data management, analytics, integration, and future trends. Get ready to unlock the full potential of CRM and elevate your service organization to new heights.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Overview
In the realm of services, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) emerges as a strategic approach to managing interactions with customers throughout their lifecycle. CRM empowers service organizations to gain a comprehensive understanding of their customers’ needs, preferences, and behaviors, enabling them to tailor their offerings and build lasting relationships.
CRM implementation within service organizations yields a plethora of benefits, including enhanced customer satisfaction, increased revenue generation, streamlined operations, and improved employee productivity. By leveraging CRM systems, service providers can automate tasks, track customer interactions, and analyze data to identify opportunities for improvement.
Examples of CRM Software and Solutions
The market offers a wide range of CRM software and solutions tailored to the specific needs of service organizations. Some notable examples include:
- Salesforce Service Cloud
- Zoho CRM
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Service
- Oracle Service Cloud
- SAP Hybris Cloud for Customer Service
These solutions provide comprehensive functionality for managing customer interactions, including case management, knowledge base management, self-service portals, and reporting and analytics.
CRM Implementation for Service Businesses
Implementing a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is crucial for service businesses to enhance customer interactions, streamline operations, and boost revenue. Here’s a comprehensive overview of the key steps involved, challenges, considerations, and best practices for successful CRM implementation.
The implementation process typically involves:
- Define Business Objectives:Clearly outlining the goals and objectives that the CRM system should help achieve.
- Select the Right CRM System:Choosing a system that aligns with the business’s specific needs, industry, and size.
- Data Migration and Integration:Importing and organizing existing customer data into the new CRM system.
- System Configuration:Customizing the CRM system to match the business’s unique processes and workflows.
- User Training and Adoption:Ensuring that employees are adequately trained on the system and actively using it.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Evaluation:Regularly assessing the CRM system’s performance and making adjustments as needed.
Challenges and Considerations for Service Businesses, Crm in services
Service businesses face unique challenges during CRM implementation, including:
- Complexity of Service Offerings:Managing diverse service offerings and their associated processes can be complex.
- Customer Relationship Management:Building and maintaining strong customer relationships is paramount in service-oriented businesses.
- Integration with Other Systems:CRM systems need to seamlessly integrate with other business applications, such as billing and scheduling.
- Data Security and Compliance:Ensuring the security and privacy of customer data is crucial in the service industry.
Best Practices for Successful CRM Implementation
To ensure successful CRM implementation, service businesses should consider the following best practices:
- Involve Key Stakeholders:Engage key stakeholders from different departments to gather their input and ensure buy-in.
- Establish Clear Metrics:Define specific metrics to measure the success of the CRM implementation.
- Provide Ongoing Support:Offer continuous training and support to users to foster adoption and maximize system utilization.
- Seek External Expertise:Consider consulting with CRM experts to guide the implementation process and provide ongoing support.
CRM Data Management

Data management is the cornerstone of effective CRM, as it enables businesses to collect, organize, and analyze customer information to gain valuable insights. A well-managed CRM system provides a comprehensive view of customer interactions, preferences, and behavior, empowering businesses to make informed decisions and enhance customer experiences.
CRM systems collect and store a wide range of data, including:
- Customer contact information (name, email, phone number, address)
- Purchase history and preferences
- Communication history (emails, phone calls, chats)
- Customer support interactions
- Website and social media activity
Data governance and security are critical aspects of CRM data management. Businesses must establish clear policies and procedures to ensure the accuracy, integrity, and security of customer data. This includes:
- Defining data ownership and access permissions
- Implementing data security measures (encryption, firewalls, intrusion detection)
- Establishing data backup and recovery plans
- Regularly auditing and reviewing data management practices
CRM Analytics and Reporting
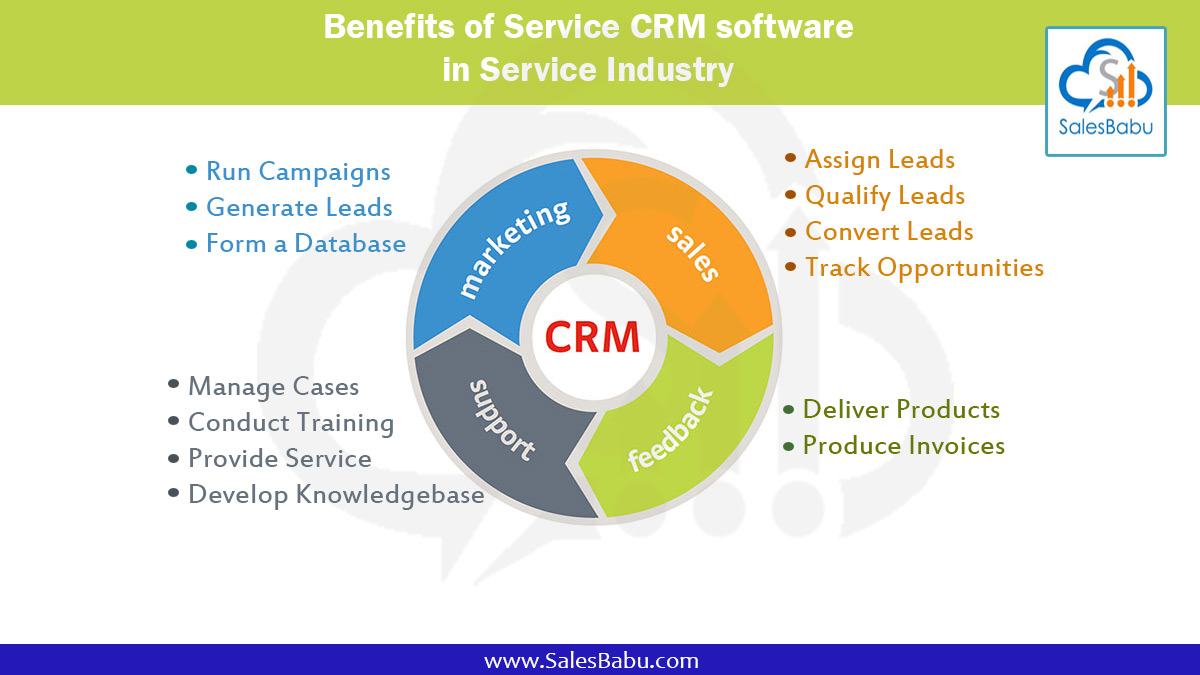
CRM analytics and reporting play a crucial role in maximizing the value of CRM data by providing insights into customer behavior, trends, and opportunities. Through data analysis and reporting, businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of their customers, enabling them to make informed decisions, improve customer satisfaction, and drive growth.
Types of Reports and Insights
CRM systems generate a wide range of reports that provide valuable insights into various aspects of customer interactions. These reports can be customized to meet specific business needs and may include:
- Sales reports:Track sales performance, identify top-performing products/services, and analyze sales trends.
- Marketing reports:Monitor campaign effectiveness, measure customer engagement, and optimize marketing strategies.
- Customer service reports:Analyze customer interactions, identify common issues, and assess the efficiency of support channels.
- Customer churn reports:Identify customers at risk of leaving and develop strategies to reduce churn.
- Customer lifetime value reports:Estimate the potential revenue and profitability of each customer over their lifetime.
Using CRM Data for Decision-Making
The insights derived from CRM analytics can be leveraged to make data-driven decisions across various business functions:
- Sales:Optimize sales processes, identify high-value leads, and forecast revenue more accurately.
- Marketing:Personalize marketing campaigns, target the right customers, and measure the ROI of marketing initiatives.
- Customer service:Improve customer satisfaction by identifying pain points, resolving issues efficiently, and providing proactive support.
- Product development:Identify customer needs, gather feedback, and develop products/services that meet market demand.
- Business strategy:Gain a comprehensive understanding of customer behavior, market trends, and competitive dynamics to make strategic decisions that drive growth.
CRM Integration with Other Systems: Crm In Services
Integrating Customer Relationship Management (CRM) with other business systems streamlines operations, enhances data accuracy, and provides a comprehensive view of customer interactions.
Benefits of CRM Integration:
- Improved data accuracy and consistency:Centralized data eliminates redundancies and ensures consistent customer information across systems.
- Enhanced customer service:Integrated systems provide a complete customer history, enabling agents to deliver personalized and efficient support.
- Increased operational efficiency:Automated processes reduce manual tasks, freeing up staff for more strategic initiatives.
Challenges and Considerations for Integration:
- Data compatibility:Ensuring data formats and structures align between systems can be complex.
- Technical expertise:Integration requires technical skills and resources to configure and maintain.
- Data security:Integrating systems involves sharing sensitive customer data, necessitating robust security measures.
Best Practices for Successful CRM Integration:
- Define clear integration goals:Identify specific objectives and benefits to drive the integration process.
- Map data fields and processes:Establish clear mappings between CRM and other systems to ensure seamless data flow.
- Utilize integration tools:Leverage software and services that simplify the integration process and automate data transfer.
- Test and monitor integration:Thoroughly test the integration and monitor its performance to identify and resolve any issues.
- Seek professional assistance:Consider consulting with experienced integrators or CRM vendors for guidance and support.
CRM Trends and Future Developments
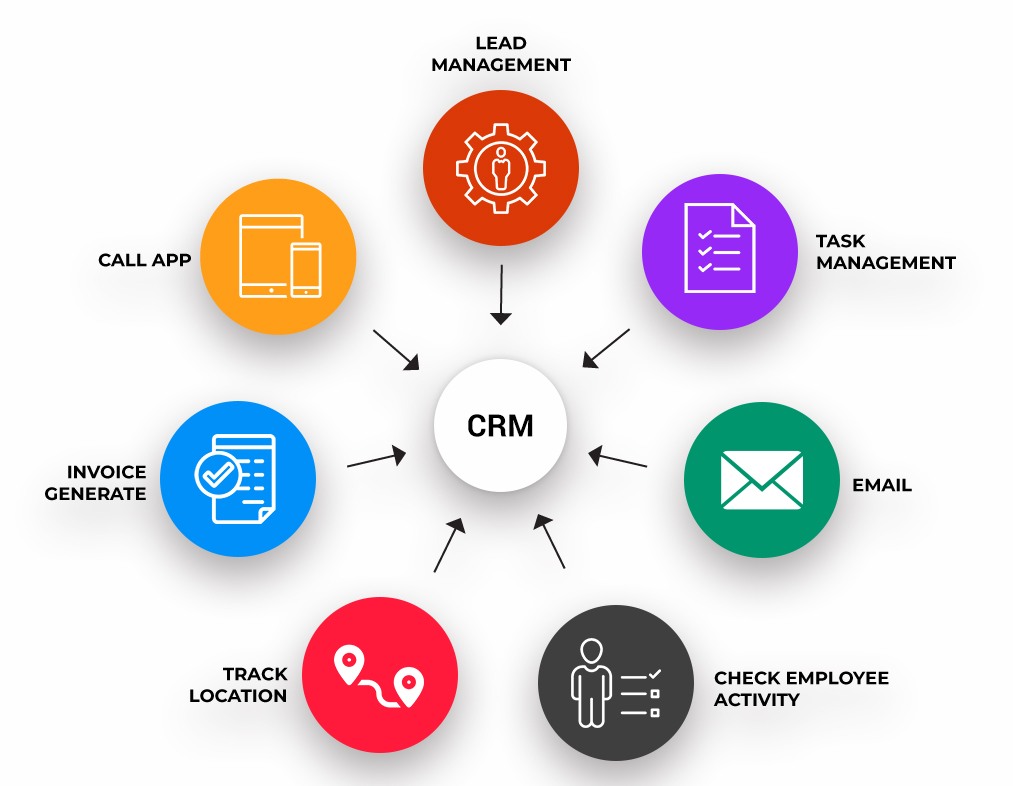
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) technology is continuously evolving, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and other emerging technologies. These trends are shaping the future of CRM and its role in service businesses.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning on CRM
AI and ML are revolutionizing CRM by automating tasks, improving data analysis, and personalizing customer experiences. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide 24/7 customer support, while ML algorithms can analyze customer data to identify patterns and trends, enabling businesses to tailor their services accordingly.
The Future of CRM in Service Businesses
CRM will continue to play a vital role in service businesses by providing a centralized platform for managing customer interactions, automating processes, and gaining insights into customer behavior. As technology advances, CRM systems will become more integrated with other business applications, such as marketing automation and salesforce automation, to create a seamless customer experience across all channels.
Conclusion
In conclusion, CRM in services is an indispensable tool for organizations seeking to excel in customer-centricity. By embracing the latest trends and leveraging the power of data, businesses can create personalized experiences, drive operational efficiency, and foster long-lasting customer relationships.
As the future of CRM unfolds, service organizations that invest in this technology will be well-positioned to thrive in an increasingly competitive landscape.