Application CRM, a game-changer in the realm of customer relationship management, takes center stage as we delve into its transformative capabilities. Its comprehensive features and benefits empower businesses to forge deeper connections, enhance efficiency, and elevate their customer experiences to unprecedented heights.
From automating tasks to streamlining processes, application CRM serves as a cornerstone for organizations seeking to build lasting relationships with their clientele. As we explore the intricate details of this transformative tool, prepare to be captivated by its potential to revolutionize your approach to customer engagement.
Overview of CRM Applications
Customer relationship management (CRM) applications are designed to help businesses manage and track their interactions with customers and potential customers. These applications provide a centralized platform for storing and organizing customer data, such as contact information, purchase history, and communication history.
CRM applications can help businesses improve their customer service, sales, and marketing efforts. By providing a complete view of each customer’s interactions with the business, CRM applications can help businesses identify opportunities to upsell or cross-sell products or services, provide personalized customer service, and develop targeted marketing campaigns.
Key Features and Capabilities of CRM Systems
CRM applications typically offer a wide range of features and capabilities, including:
- Contact management: Store and organize customer contact information, including name, address, phone number, and email address.
- Lead management: Track and manage potential customers through the sales pipeline.
- Opportunity management: Track and manage sales opportunities from initial contact to close.
- Customer service management: Manage customer service requests and track customer interactions.
- Marketing automation: Automate marketing campaigns and track results.
- Reporting and analytics: Generate reports and analyze data to track progress and identify areas for improvement.
Types of CRM Applications
Customer relationship management (CRM) applications offer a diverse range of solutions to meet the specific needs of businesses. Each type of CRM application provides unique features and benefits, catering to different aspects of customer interactions and relationship management.
Operational CRM
Operational CRM focuses on automating and streamlining day-to-day customer interactions. It includes:
- Sales force automation (SFA):Manages sales activities, including lead generation, tracking, and forecasting.
- Marketing automation:Automates marketing campaigns, lead nurturing, and email marketing.
- Customer service management:Provides tools for handling customer inquiries, resolving issues, and tracking customer interactions.
Analytical CRM
Analytical CRM analyzes customer data to provide insights and improve decision-making. It includes:
- Data warehousing:Stores and organizes customer data from various sources.
- Data mining:Discovers patterns and trends in customer data to identify opportunities and risks.
- Reporting and analytics:Generates reports and dashboards to provide real-time insights into customer behavior.
Collaborative CRM
Collaborative CRM facilitates communication and collaboration among different teams and departments within an organization. It includes:
- Team collaboration:Provides tools for sharing information, managing projects, and tracking progress.
- Partner relationship management (PRM):Manages relationships with partners, distributors, and suppliers.
- Social CRM:Integrates social media channels into CRM systems to monitor customer sentiment and engage with customers.
Strategic CRM
Strategic CRM focuses on long-term customer relationship building and growth. It includes:
- Customer segmentation:Divides customers into groups based on their needs and characteristics.
- Customer loyalty programs:Rewards customers for their loyalty and encourages repeat business.
- Customer lifetime value (CLTV):Calculates the total value of a customer over their lifetime.
Benefits of CRM Applications
CRM applications offer numerous tangible and intangible benefits that can significantly improve business outcomes. By centralizing customer data and automating processes, businesses can enhance customer relationships, increase efficiency, and drive growth.
Tangible Benefits
- Improved customer satisfaction:CRM systems provide a comprehensive view of customer interactions, enabling businesses to identify and address customer needs promptly. This leads to enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Increased sales revenue:CRM applications automate sales processes, streamline communication, and provide insights into customer preferences. This enables sales teams to close deals faster and generate more revenue.
- Reduced operating costs:CRM systems automate repetitive tasks, reducing the need for manual labor. This frees up resources for more strategic initiatives and reduces overall operating costs.
Intangible Benefits
- Enhanced decision-making:CRM systems provide data-driven insights into customer behavior and preferences. This information empowers businesses to make informed decisions that drive growth and improve customer experiences.
- Improved collaboration:CRM applications facilitate collaboration between different departments, such as sales, marketing, and customer support. This seamless information sharing improves communication and ensures that customers receive consistent and personalized experiences.
- Increased customer retention:CRM systems enable businesses to track customer interactions and identify opportunities for engagement. By proactively reaching out to customers, businesses can build stronger relationships and reduce churn.
Challenges of Implementing CRM Applications: Application Crm
Implementing CRM applications is not without its challenges. Organizations may encounter various obstacles and pitfalls during the implementation process. These challenges can range from technical issues to organizational resistance and require careful planning and mitigation strategies to ensure successful implementation.
Technical Challenges
Technical challenges can arise from compatibility issues between the CRM system and existing software, data integration complexities, and performance bottlenecks. Ensuring compatibility and seamless data flow between the CRM system and other business applications is crucial. Organizations should conduct thorough due diligence and testing before implementation to minimize technical glitches and ensure smooth operation.
Organizational Resistance
Organizational resistance can be a significant challenge, as employees may be reluctant to adopt new technology or may have concerns about the impact on their roles and responsibilities. Effective communication, training, and change management strategies are essential to address these concerns, gain user buy-in, and foster a positive attitude towards the CRM implementation.
Data Quality Issues
CRM applications rely heavily on accurate and up-to-date data. Poor data quality can lead to inaccurate insights, ineffective marketing campaigns, and compromised customer relationships. Organizations should establish robust data governance processes, implement data cleansing and validation mechanisms, and ensure ongoing data maintenance to maintain data integrity and reliability.
Lack of Integration
Lack of integration between the CRM system and other business applications can create silos and hinder information sharing. Organizations should ensure that the CRM system integrates seamlessly with other systems, such as ERP, marketing automation, and customer service platforms, to facilitate a holistic view of customer interactions and enable seamless data flow across departments.
Cost and Resource Considerations
CRM implementation can be a costly and resource-intensive endeavor. Organizations need to carefully consider the financial implications and allocate sufficient resources to cover software licensing, hardware upgrades, training, and ongoing maintenance costs. Failure to plan adequately for these expenses can lead to budget overruns and project delays.
Trends in CRM Applications
The CRM industry is constantly evolving, with new trends and advancements emerging all the time. These trends are shaping the future of CRM applications, making them more powerful and user-friendly than ever before.
One of the most important trends in CRM is the move towards cloud-based applications. Cloud-based CRM applications are hosted on the internet, which means that businesses can access them from anywhere with an internet connection. This makes it much easier for businesses to manage their customer relationships, as they can do so from any location.
Another important trend in CRM is the use of artificial intelligence (AI). AI can be used to automate many tasks in CRM, such as lead generation, customer segmentation, and customer service. This can free up businesses to focus on more strategic tasks, such as building relationships with customers.
Finally, the trend towards mobile CRM is also gaining momentum. Mobile CRM applications allow businesses to manage their customer relationships from their smartphones or tablets. This makes it even easier for businesses to stay connected with their customers, as they can do so from anywhere.
Integration with Other Business Systems
CRM applications are becoming increasingly integrated with other business systems, such as ERP and marketing automation systems. This integration allows businesses to get a complete view of their customers, and to manage all of their customer interactions from a single platform.
Personalization
CRM applications are becoming increasingly personalized, allowing businesses to tailor the application to their specific needs. This includes the ability to customize the user interface, add custom fields, and create custom reports.
Self-Service Portals
CRM applications are increasingly offering self-service portals, which allow customers to access their own account information and resolve their own issues. This can help to reduce the workload for customer service teams, and improve the customer experience.
Case Studies and Examples
To demonstrate the effectiveness of CRM applications, let’s explore real-world case studies and examples of successful implementations.
These case studies highlight the specific strategies and tactics employed to achieve positive results, showcasing the transformative power of CRM in various industries.
Starbucks’ Customer-Centric Approach
Starbucks, the global coffeehouse chain, implemented a CRM program that focused on creating personalized customer experiences.
Through its mobile app and loyalty program, Starbucks gathered customer data, such as purchase history, preferences, and location, to tailor marketing campaigns and provide personalized recommendations.
This data-driven approach resulted in increased customer engagement, loyalty, and sales.
Salesforce’s Cloud-Based Success
Salesforce, a leading CRM software provider, has implemented its own CRM solution to manage its sales, marketing, and customer service operations.
By leveraging the cloud-based platform, Salesforce gained agility, scalability, and real-time access to customer data, enabling its teams to collaborate more effectively and respond quickly to customer needs.
This implementation has contributed to Salesforce’s consistent growth and industry leadership.
Amazon’s Data-Driven Dominance
Amazon, the e-commerce giant, utilizes a robust CRM system to manage its vast customer base and provide seamless shopping experiences.
Amazon collects and analyzes customer data from every touchpoint, including purchase history, browsing behavior, and product reviews.
This data is used to personalize product recommendations, offer tailored promotions, and provide exceptional customer support, driving customer loyalty and increased sales.
Best Practices for CRM Applications
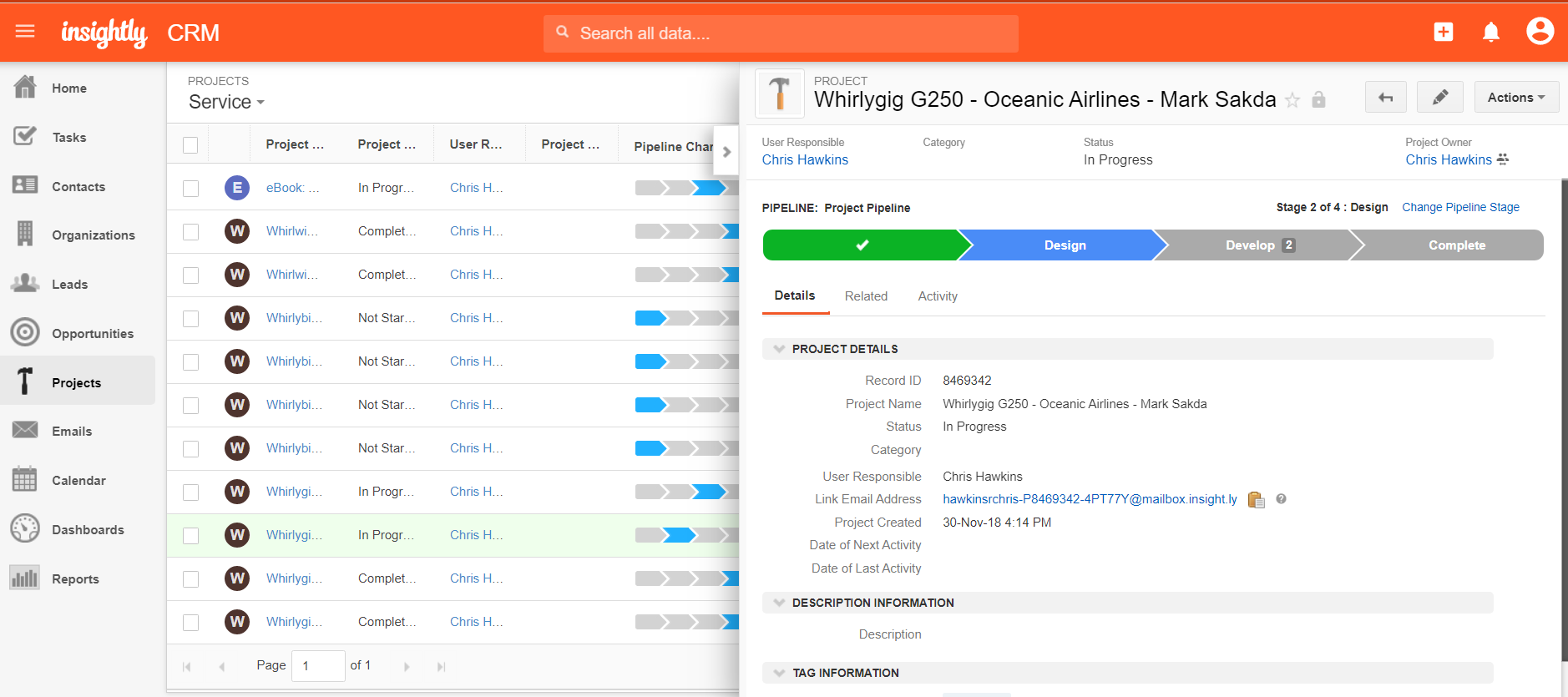
Implementing and managing CRM applications effectively is crucial for businesses to maximize their ROI and ensure ongoing success. Here are some best practices to consider:
Strategy and Planning:Define clear business objectives and goals before implementing a CRM system. Identify the specific processes and areas that the CRM will support and align it with the overall business strategy.
Data Management
- Establish a comprehensive data governance plan to ensure data accuracy, consistency, and security.
- Implement data integration strategies to connect the CRM with other business systems and eliminate data silos.
- Regularly cleanse and update customer data to maintain its integrity and relevance.
Process Optimization
- Analyze existing sales, marketing, and customer service processes to identify areas for improvement.
- Automate repetitive tasks and workflows to streamline operations and increase efficiency.
- Establish clear roles and responsibilities for CRM users to ensure accountability and collaboration.
User Adoption and Training
- Provide comprehensive training and support to ensure users understand the CRM’s capabilities and benefits.
- Foster a culture of CRM adoption by promoting its value and demonstrating its impact on business outcomes.
- Regularly gather feedback from users to identify areas for improvement and address any concerns.
Continuous Improvement
- Regularly review and assess the CRM’s performance against key metrics and business objectives.
- Identify opportunities for optimization and enhancements based on data analysis and user feedback.
- Stay updated with the latest CRM trends and technologies to ensure the system remains effective and competitive.
Integration with Other Business Systems
Integrating CRM applications with other business systems is crucial for streamlining operations and enhancing data accuracy. It enables a holistic view of customer interactions and facilitates seamless data flow across various departments.By integrating CRM with accounting systems, businesses can automate order processing, invoice generation, and payment tracking.
This integration eliminates manual data entry, reduces errors, and improves efficiency. Additionally, integrating with marketing automation platforms allows for targeted campaigns based on customer data, resulting in improved lead generation and conversion rates.
Successful Integrations and Benefits
A notable example of successful CRM integration is the collaboration between Salesforce and Microsoft Dynamics 365. This integration provides a comprehensive view of customer data, allowing businesses to manage sales, marketing, and customer service from a single platform. It enhances collaboration between teams and improves customer experience.Another successful integration is between Zoho CRM and Google Workspace.
This integration enables seamless access to customer data from within Gmail, Google Calendar, and other Workspace applications. It simplifies communication, task management, and scheduling, increasing productivity and efficiency.
Customization and Customization Options
Customizing CRM applications is crucial to align them with specific business requirements and optimize their effectiveness. By tailoring the system to unique processes, workflows, and data structures, businesses can enhance user adoption, improve data accuracy, and streamline operations.
Effective customization involves understanding business needs, defining customization goals, and leveraging the CRM system’s customization capabilities. This includes configuring fields, creating custom objects, developing custom reports and dashboards, and integrating with external systems.
Customization Considerations
- Identify the specific business processes and requirements that need to be addressed.
- Assess the capabilities of the CRM system and determine if it can meet the customization needs.
- Consider the impact of customization on system performance, maintenance, and future upgrades.
- Involve key stakeholders and end-users in the customization process to ensure their input and feedback.
- Document the customization process thoroughly for future reference and maintenance.
Future of CRM Applications
The future of CRM applications is promising, with emerging technologies and trends set to revolutionize how businesses manage customer relationships.
One of the most significant trends is the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). AI-powered CRM systems can automate tasks, provide insights, and make predictions that help businesses better understand and serve their customers.
Impact on Businesses, Application crm
The future of CRM applications will have a profound impact on businesses. By leveraging AI, ML, and other emerging technologies, businesses can:
- Improve customer experience by providing personalized and proactive service
- Increase sales and marketing efficiency by automating tasks and generating leads
- Gain insights into customer behavior and preferences to make better decisions
- Reduce costs by automating tasks and streamlining processes
Closing Notes
In the tapestry of modern business, application CRM emerges as an indispensable thread, weaving together customer data, insights, and interactions to create a vibrant and responsive tapestry. Its impact extends beyond mere data management, fostering personalized experiences, driving informed decision-making, and propelling businesses towards unparalleled success.
As we bid farewell to this exploration, let us embrace the transformative power of application CRM, recognizing its ability to redefine customer relationships and propel organizations to the forefront of their industries. May its implementation ignite a new era of customer-centricity, driving growth, innovation, and enduring success.