As CRM in management takes center stage, it empowers organizations to forge enduring customer relationships, streamline operations, and drive business growth. Delve into this comprehensive guide to unravel the transformative power of CRM and its impact on modern business practices.
CRM systems serve as the cornerstone of customer-centric organizations, enabling businesses to manage interactions, track preferences, and personalize experiences. By harnessing the power of data and automation, CRM empowers organizations to deliver exceptional customer service, boost sales, and gain a competitive edge.
CRM Definition and Overview
Customer relationship management (CRM) is a business strategy that focuses on building and maintaining profitable customer relationships. It involves managing all aspects of customer interactions, from initial contact to ongoing support, with the goal of improving customer satisfaction, loyalty, and profitability.CRM systems are software applications that help businesses manage their customer relationships.
These systems can track customer interactions, store customer data, and automate marketing and sales processes. By providing a central repository for customer information, CRM systems can help businesses improve their customer service, increase sales, and reduce costs.
Examples of CRM Systems, Crm in management
There are many different CRM systems available on the market, each with its own unique features and benefits. Some of the most popular CRM systems include Salesforce, HubSpot, and Microsoft Dynamics CRM.The best CRM system for a particular business will depend on its specific needs and requirements.
However, all CRM systems share some common features, such as:
- Contact management: CRM systems allow businesses to track and manage all of their customer contacts, including their names, addresses, phone numbers, and email addresses.
- Sales tracking: CRM systems can help businesses track their sales pipeline, from lead generation to close. This information can help businesses identify opportunities for growth and improve their sales performance.
- Marketing automation: CRM systems can help businesses automate their marketing campaigns, such as email marketing, social media marketing, and web marketing. This can help businesses save time and money, while also improving the effectiveness of their marketing efforts.
- Customer service: CRM systems can help businesses provide better customer service by tracking customer interactions and providing customer support representatives with the information they need to resolve customer issues quickly and efficiently.
CRM systems can be a valuable tool for businesses of all sizes. By implementing a CRM system, businesses can improve their customer relationships, increase sales, and reduce costs.
Types of CRM Systems
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are designed to manage and analyze customer interactions and data. Different types of CRM systems cater to specific business needs and objectives.
There are three main types of CRM systems:
Operational CRM
Operational CRM focuses on automating and streamlining day-to-day customer-facing processes. It includes:
- Sales force automation: Manages sales activities, such as lead generation, tracking, and closing.
- Marketing automation: Automates marketing campaigns, email marketing, and social media management.
- Customer service automation: Provides tools for managing customer inquiries, complaints, and support.
Analytical CRM
Analytical CRM analyzes customer data to gain insights and improve decision-making. It includes:
- Data warehousing: Stores and organizes customer data from various sources.
- Data mining: Analyzes customer data to identify patterns, trends, and customer segments.
- Reporting and dashboards: Provides real-time insights and performance metrics.
Collaborative CRM
Collaborative CRM facilitates collaboration and communication between different departments within an organization. It includes:
- Team collaboration: Allows teams to share customer information, notes, and activities.
- Partner relationship management: Manages relationships with external partners, such as distributors and suppliers.
- Social CRM: Integrates social media platforms to monitor customer sentiment and engage with customers.
Benefits of CRM in Management
CRM systems offer numerous advantages for organizations, revolutionizing customer interactions and optimizing business processes.
By leveraging CRM, businesses can significantly enhance customer satisfaction, streamline operations, and boost revenue generation.
Improved Customer Satisfaction
- CRM enables businesses to gain a comprehensive understanding of customer preferences, purchase history, and communication channels.
- This in-depth knowledge allows organizations to tailor personalized experiences, resolve issues promptly, and proactively address customer needs.
Streamlined Operations
- CRM integrates various departments and functions within an organization, breaking down silos and facilitating seamless collaboration.
- Automated workflows, centralized data, and real-time insights empower teams to work more efficiently and effectively.
Increased Revenue
- CRM helps identify cross-selling and upselling opportunities, allowing businesses to maximize customer lifetime value.
- Targeted marketing campaigns based on customer data enhance conversion rates and drive sales growth.
According to a study by Salesforce, companies that implement CRM systems experience an average increase of 12% in revenue.
Another study by Aberdeen Group found that organizations with a mature CRM strategy achieve a 71% higher customer retention rate than those without.
Challenges of CRM Implementation: Crm In Management
Implementing CRM systems can be a complex and challenging endeavor for organizations. Several potential obstacles can arise during the implementation process, which must be carefully addressed to ensure a successful outcome.
Common challenges associated with CRM implementation include:
Data Integration
- Integrating data from multiple sources, such as legacy systems, spreadsheets, and external databases, can be a significant challenge.
- Data inconsistencies, duplicates, and missing values can hinder the accuracy and reliability of the CRM system.
- Organizations need to develop robust data integration strategies and invest in data cleansing and standardization processes to overcome these challenges.
User Adoption
- Getting users to adopt and utilize the CRM system effectively is crucial for its success.
- Resistance to change, lack of training, and a poor user interface can hinder user adoption.
- Organizations should provide comprehensive training, involve users in the implementation process, and ensure the CRM system aligns with their workflows and needs.
Cost Considerations
- CRM implementation can involve significant upfront costs, including software licensing, hardware, and consulting services.
- Ongoing maintenance and support costs also need to be factored in.
- Organizations should carefully evaluate the cost-benefit analysis and ensure that the potential return on investment justifies the expenses.
Best Practices for CRM Management
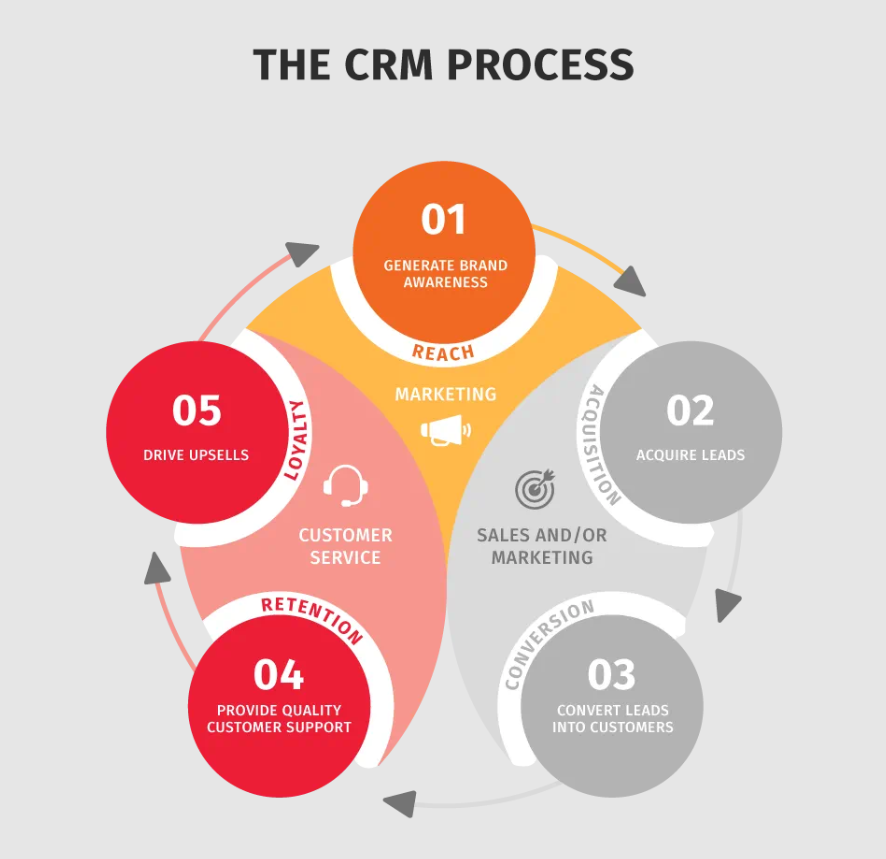
Effectively managing CRM systems requires a combination of strategic planning, data-driven decision-making, and continuous improvement. Best practices in CRM management focus on optimizing data management, streamlining processes, and monitoring performance to drive business growth and customer satisfaction.
To ensure successful CRM implementation, organizations should adopt industry standards and stay abreast of emerging trends in CRM technology and practices. By following these best practices, businesses can maximize the value of their CRM systems and achieve their customer relationship management goals.
Data Management
Data management is the foundation of effective CRM. Organizations should establish clear data governance policies and processes to ensure data accuracy, consistency, and accessibility. This includes implementing data cleansing and standardization procedures, as well as establishing data security measures to protect sensitive customer information.
- Implement data governance policies and procedures to ensure data quality and compliance.
- Regularly cleanse and standardize data to improve data accuracy and usability.
- Establish robust data security measures to protect customer information.
- Integrate CRM data with other business systems to provide a comprehensive view of customer interactions.
Process Optimization
Streamlining CRM processes can significantly improve efficiency and productivity. Organizations should identify and eliminate redundant or inefficient processes, and implement automation tools to streamline workflows. By optimizing processes, businesses can reduce operational costs, improve customer response times, and enhance the overall customer experience.
- Identify and eliminate redundant or inefficient processes to streamline workflows.
- Implement automation tools to automate repetitive tasks and improve efficiency.
- Establish clear process ownership and accountability to ensure process adherence.
- Regularly review and update processes to incorporate best practices and industry standards.
Performance Monitoring
Regularly monitoring CRM performance is crucial for identifying areas of improvement and ensuring that the system is meeting business objectives. Organizations should establish key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with their CRM goals and track progress over time. By analyzing CRM performance data, businesses can make informed decisions to improve system effectiveness and drive better outcomes.
- Establish clear KPIs that align with CRM goals and business objectives.
- Track CRM performance data regularly to identify areas of improvement.
- Use analytics tools to analyze CRM data and gain insights into customer behavior.
- Make data-driven decisions to improve CRM system effectiveness and drive better outcomes.
Industry Standards and Emerging Trends
To stay competitive, organizations should adopt industry standards and stay abreast of emerging trends in CRM management. Industry standards provide a framework for best practices and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Emerging trends, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and customer experience (CX) analytics, offer opportunities to enhance CRM capabilities and drive innovation.
- Adopt industry standards to ensure best practices and compliance.
- Stay abreast of emerging trends in CRM technology and practices.
- Explore the use of AI, ML, and CX analytics to enhance CRM capabilities.
- Attend industry events and webinars to learn about new trends and best practices.
CRM Integration with Other Business Systems
Integrating CRM systems with other business applications is crucial for seamless data sharing and process automation. This enables a comprehensive view of customer interactions, streamlines workflows, and improves operational efficiency.
By connecting CRM with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, businesses can align customer data with inventory management, order fulfillment, and financial operations. This integration ensures accurate and timely order processing, reduces errors, and improves customer satisfaction.
Benefits of CRM Integration
- Seamless data sharing eliminates data silos and provides a unified customer view.
- Automated workflows streamline processes, such as lead generation, sales follow-ups, and customer support.
- Improved collaboration between sales, marketing, and customer service teams.
- Increased efficiency and productivity, leading to cost savings and improved ROI.
Examples of Successful CRM Integrations
- Salesforce and SAP:Integrated CRM with ERP to streamline lead-to-cash processes, improve sales forecasting, and enhance customer service.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 and Adobe Experience Cloud:Integrated CRM with marketing automation to personalize customer experiences, track campaign performance, and improve lead conversion rates.
Future Trends in CRM
Emerging trends and innovations in CRM technology are reshaping the way businesses manage customer relationships. Artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and data analytics are driving advancements that enhance customer experiences, streamline operations, and provide valuable insights.
Artificial Intelligence
AI-powered CRM systems automate tasks, provide personalized recommendations, and improve customer engagement. Chatbots and virtual assistants offer 24/7 support, while machine learning algorithms analyze customer data to identify trends, predict behavior, and deliver tailored experiences.
Cloud Computing
Cloud-based CRM systems offer flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Businesses can access their CRM data from anywhere, on any device, without the need for on-premises infrastructure. Cloud computing also enables seamless integration with other business applications, such as ERP and marketing automation.
Data Analytics
Data analytics plays a crucial role in CRM by providing businesses with insights into customer behavior, preferences, and trends. Advanced analytics techniques, such as predictive modeling and sentiment analysis, help businesses understand customer needs, identify opportunities, and make informed decisions.
Last Recap
In conclusion, CRM in management is an indispensable tool for organizations seeking to elevate their customer relationships and drive business success. By embracing best practices, leveraging emerging technologies, and fostering a data-driven culture, organizations can unlock the full potential of CRM and transform their customer engagement strategies.